Rowe EDU - Water Profile
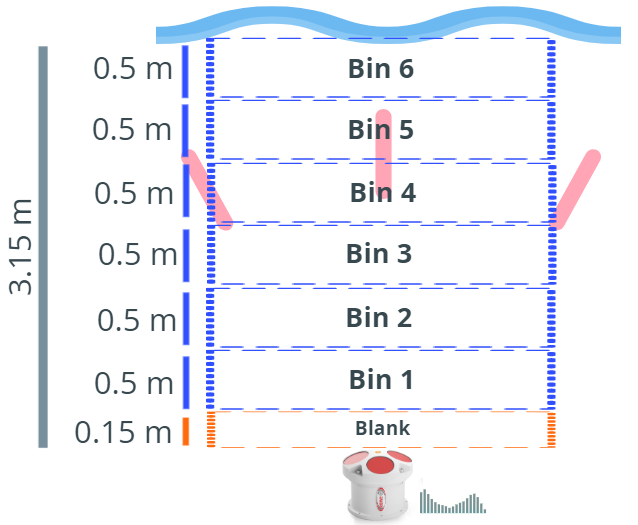
Introduction A water profile measurement is a profile of a water column that gives the direction and speed of the water currents. Water Profile Description Bins So to create a water profile measurement, the water column must be broken up into bins (cells). The bin sizes and number of bins are set by the user using the CWPBS command and CWPBN commands. Blank The Blank area is the area before the first bin to ignore.